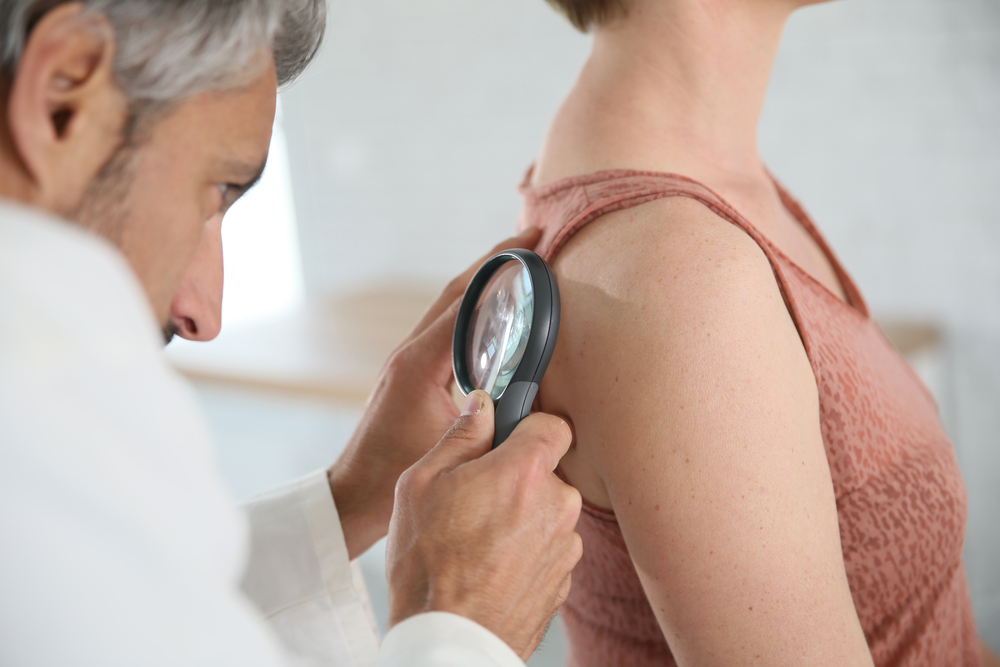
Merck and Moderna recently announced that an investigational personalized cancer vaccine (mRNA-4157) continued to show improvement at a three-year preplanned analysis of Relapse Free Survival when combined with Keytruda. The combination showed continued improvement in recurrence free survival and distant metastasis-free survival (DFS) of patients with high-risk melanoma.
The risk of distant metastasis or death at a preplanned two-year analysis was reduced by 65%.
Data for the primary analysis presented at ASCO and AACR in 2023, showed that there was a 44% reduction of recurrence or death in combined KEYTRUDA and mRNA-4157. Keytruda is characterized as an immunotherapy that aids the body’s immune system in the fight against tumor cells.
Furthermore, the combination of mRNA-4157 (V940) and KEYTRUDA produced a 65% reduction in death or metastasis.
Going Forward
Phase 3 studies in adjuvant settings have recently been launched for high-risk melanoma patients and patients with non-small cell lung cancer. These companies will rapidly expand to other tumor types. Adjuvant therapy, using common anticancer treatments, attacks cancer cells that the initial cancer treatment did not eliminate. The chance of having a relapse is reduced through adjuvant therapy. As new cancer treatment continues to evolve, the focus is on individual, personalized cancer therapies. Researchers are using the patient’s tumor mutation to develop a treatment unique to the patient.
Editor’s Note: Get Involved!
Cancer doesn’t discriminate. WHATNEXT and its partners are interested in amplifying the voices of those from all identities and backgrounds. If you have a cancer journey to share, reach out here to learn more about how your voice can help spread awareness and inspire individuals from all walks of life.
About Neoantigens
Neoantigens are recognized as foreign proteins that do not exist in normal tissue. They are recognized by the immune system as “non self” and thereby stimulate the patient’s immune system to attack the cancer. Neoantigens use a person’s tumor biopsy sample in the development of therapies unique to their tumor mutation.
About Adverse Events
Reported adverse events in the mRNA-4157 trial (V940) KEYNOTE-942 in a median planned three-year follow-up were consistent with previously reported results.
Reported treatment-related Grade ≥3 adverse events were similar: mRNA 4157 combined with KEYTRUDA (25%) vs. KEYTRUDA alone (20%). Three of the most common adverse events were reported in connection with mRNA-4157. They were fatigue, pain at the injection site, and chills.
Merck and Moderna announced the launch of Phase 3 INTerpath-001 (V940-001) in July 2023. The trial (NCT05933577) evaluates mRNA-4157 combined with adjuvant treatment for patients categorized as having high-risk melanoma. It is currently enrolling patients globally. The two companies are also initiating; a trial (Phase 3) of non-small cell lung cancer which is also enrolling globally (INTerpath-002 (NCT06077760). Plans are underway to include other tumor types.
About mRNA-4157 (V940)
Messenger RNA is a molecule that contains the instructions or recipe that directs the cells to make a protein using its natural machinery. To enter cells smoothly, mRNA travels within a protective bubble called a lipid nanoparticle. It is based on individualized neoantigen therapy that consists of synthetic mRNA coding accommodating about thirty-four neoantigens. It is produced in accordance with the unique mutational signature of the patient’s tumor.
Once situated in the body, the RNA encoded neoantigen undergo natural cellular antigen processing. Neoantigen therapies train and activate antitumor response by stimulating T-cell responses based on the mutational signature of the patient’s tumor. The combination of mRNA-4157 (V940) with KEYTRUDA has the potential of a benefit over KEYTRUDA alone.
cancer treatment clinical trial melanoma treatment
Last modified: February 20, 2024